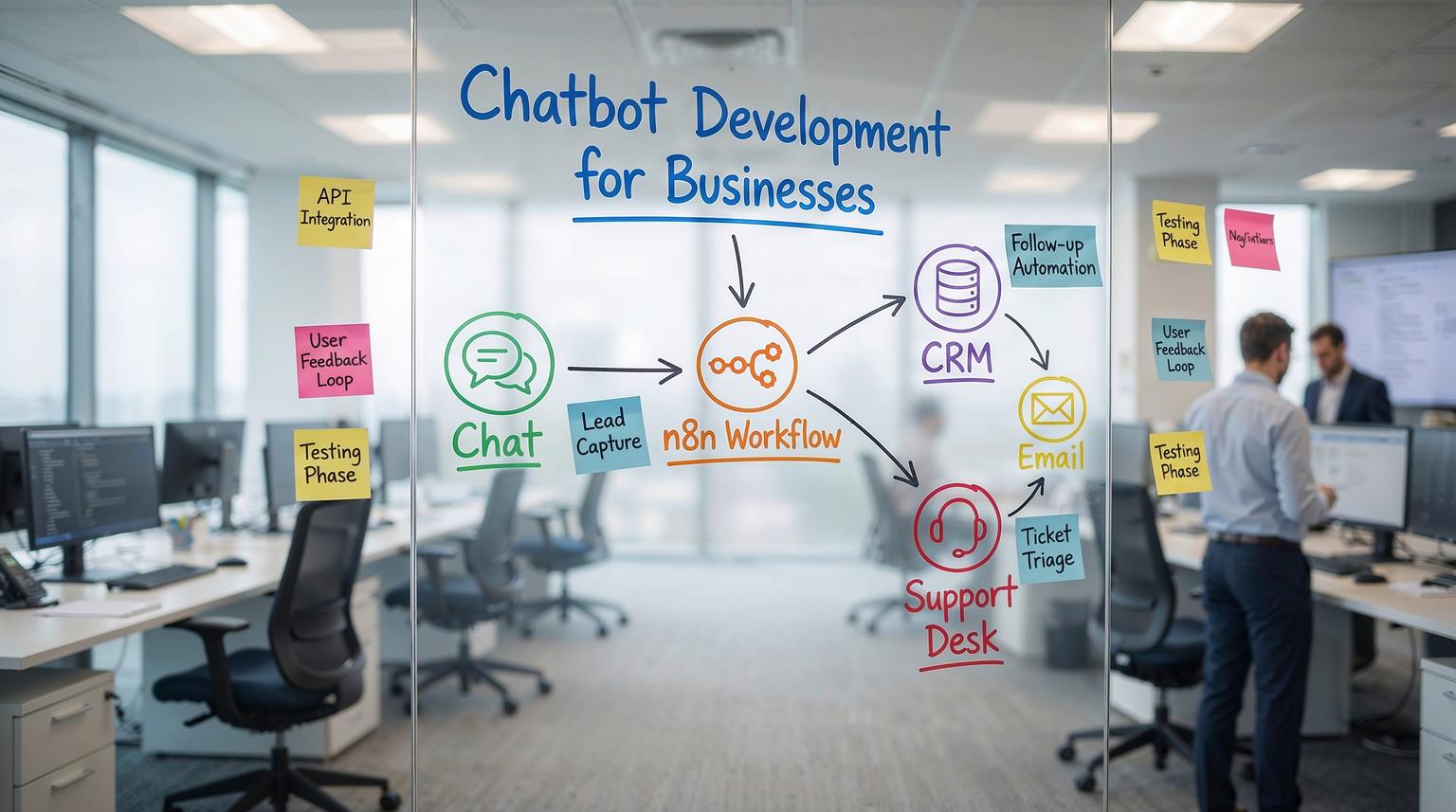
Most business chatbots fail for one simple reason, they are treated like a standalone widget instead of an operational workflow. This practical guide to chatbot development for businesses shows how we build bots at ThinkBot Agency, starting with a single support or lead capture flow then expanding into an end to end automation system that syncs data, routes tickets and triggers follow ups across your CRM, inbox and internal tools.
This is written for business owners, ops leaders and marketing or CRM teams who want measurable outcomes, fewer manual handoffs and faster response times without building a fragile pile of scripts.
At a glance:
- Start with one high volume use case, then add routing, memory and escalation.
- Design the conversation around data capture, not clever replies.
- Connect chat to CRM, email and ticketing so every message becomes an action.
- Use n8n to orchestrate multi step workflows, logging, retries and guardrails.
Quick start
- Pick one workflow to automate first, such as lead qualification or ticket triage.
- Define the minimum data you need to capture, then write the conversation steps to collect it.
- Build a simple bot that can ask, validate and confirm the captured fields.
- Connect the bot to n8n so messages trigger CRM updates, email sends and ticket routing.
- Add escalation rules and logging, then run a one week pilot and iterate.
A business ready chatbot is a conversation layer connected to your systems. You design a flow that captures intent and structured data, then use automation to create or update CRM records, route tickets to the right queue and trigger emails or tasks. Start small with one workflow, harden it with guardrails and monitoring and then expand into full customer support automation. For a broader look at how these automations connect across your stack, you can also review our guide on CRM automation with AI and end-to-end workflows.
Choose a first workflow that proves ROI fast
In 2026 most teams do not need a bot that can answer everything. They need a bot that reliably completes one job and hands off cleanly when it cannot. We typically recommend starting with one of these:
- Lead capture and qualification on your website chat or WhatsApp.
- Support triage that collects issue type, urgency, account email and order or invoice number.
- Status checks such as order status, booking confirmations or password reset guidance.
- Internal helpdesk intake in Slack or Teams for IT and ops requests.
The best first workflow has three traits, it is high volume, it is repetitive and it requires data entry in at least one system. That is where automation creates immediate lift.
Define success metrics before you build
Pick two or three measurable outcomes so you can evaluate the pilot:
- Containment rate, percent resolved without a human.
- Time to first response and time to resolution.
- Lead to meeting conversion rate for qualified leads.
- Ticket data completeness, percent of tickets with required fields.
Conversation flow design that maps to operations
Good conversation design is not about sounding human. It is about collecting the right inputs, confirming them and routing the user to the next best action. When we design flows we aim for deterministic steps first, then add AI where it helps with intent detection and summarization.
A simple flow pattern we use
- Greet and set expectations, what the bot can help with.
- Identify intent, pick from buttons or short options when possible.
- Collect required fields, one question at a time with validation.
- Confirm and summarize, show what will happen next.
- Execute automation, create ticket or lead, send confirmations.
- Escalate when needed, transfer with context and transcript.
Support triage checklist (use this before you wire anything)
Use this checklist when you are defining your first support bot workflow. If you cannot answer these, the automation will break later.
- What are the top 5 intents you will support in version 1?
- What fields are mandatory to create a ticket in your helpdesk or CRM?
- How will you validate identity, email lookup, order number, last 4 digits, magic link?
- What counts as urgent and what is the SLA target for each priority?
- Which queue or owner should each intent route to?
- What is the escalation trigger, negative sentiment, repeated failure, VIP account, explicit request for a human?
- What confirmation message and email should the user receive after submission?
- Where will transcripts be stored and who can access them?
- What is the fallback when the bot is unsure, ask a clarifying question or escalate?
- What data should never be requested in chat, passwords, full card numbers, sensitive IDs?

How to connect your chatbot to CRM and email platforms
The fastest way to turn a chatbot into revenue and support capacity is to connect it to the systems your team already uses. At ThinkBot we treat the bot as an input channel, then we use automation to keep your CRM, inbox and ticketing system in sync. If you want to go deeper into the integration side, our article on API integration for business automation with CRM, email, and AI walks through patterns that pair well with this chatbot approach.
Lead capture and qualification flow (practical mapping)
Here is a common pattern for sales and marketing teams:
- Chat collects name, email, company, use case, timeline and budget range.
- Automation checks the CRM for an existing contact and account.
- If new, create contact and lead, then assign owner based on territory or routing rules.
- Send a personalized email confirmation and optionally a calendar link.
- Notify the assigned rep in Slack or Teams with a summary and next steps.
This is where structured data matters. If the bot captures clean fields, your CRM automation becomes reliable and reporting becomes accurate.
Ticket routing and follow up flow (support)
- Chat collects issue type, product area, urgency, account email and attachments if applicable.
- Automation creates a ticket, tags it and sets priority.
- Send a confirmation email with ticket ID and expected response time.
- If VIP or urgent, alert an on call channel and assign to a senior queue.
- Store transcript and an AI summary on the ticket for faster handling.
n8n as the automation backbone for end to end support
Chat platforms are great at messaging, CRMs are great at records and email tools are great at delivery. The hard part is orchestration, retries, branching logic and audit trails. This is why we often use n8n as the workflow layer to connect everything.
What n8n gives you in production
- Routing based on intent, customer tier, sentiment or business hours.
- Data enrichment by pulling account context before responding.
- Reliable execution with retries, error handling and logging.
- API connectivity for tools without native integrations.
- Modular workflows so you can update one step without breaking the whole bot.
Example event payload for a chatbot -> n8n workflow
This is a simple schema we implement so every chat message can be processed consistently across channels.
{
"channel": "webchat",
"conversation_id": "c_9f1a2",
"message_id": "m_10493",
"timestamp": "2026-01-06T14:22:10Z",
"user": {
"name": "Sam Lee",
"email": "[email protected]",
"phone": "+15551234567",
"account_id": "",
"language": "en"
},
"intent": "support_triage",
"fields": {
"issue_type": "billing",
"urgency": "high",
"order_number": "A-18372",
"summary": "Charged twice for the same invoice"
},
"raw_text": "I was charged twice for invoice A-18372",
"attachments": [],
"consent": {
"marketing": false,
"data_processing": true
}
}
With a payload like this, n8n can branch cleanly, create or update CRM records, open tickets, send emails and write logs without guessing what the bot meant.

Where AI fits, and where it should not
We use AI for classification, summarization, sentiment detection and drafting responses. We avoid using AI for actions that must be deterministic, such as refund approvals or account changes, unless there is a strict validation step and a human approval gate.
If you are prototyping using a no code automation tool, the module based pattern is similar to what Make describes for connecting chat triggers to LLM processing and response modules, then adding routing and memory. Their step by step guide is a useful reference for the general approach, even if your production stack is n8n: step by step. For a detailed n8n-focused blueprint, see our chatbot implementation guide for customer support with n8n and AI.
Common failure modes and mitigations
Automation first chatbots fail in predictable ways. Use the guardrails below when you move from pilot to production.
Failure modes and mitigations
- Failure: The bot captures incomplete data and creates unusable CRM records. Mitigation: Add field validation, required questions and a confirmation step before submission.
- Failure: Users ask out of scope questions and the bot guesses. Mitigation: Use intent thresholds, add a safe fallback and escalate to a human when confidence is low.
- Failure: Duplicate contacts and tickets flood the system. Mitigation: Deduplicate by email and conversation_id, then update existing records instead of creating new ones.
- Failure: Escalations lose context and customers repeat themselves. Mitigation: Attach transcript, structured fields and an AI summary to the ticket and pass key variables during handoff.
- Failure: Sensitive data is collected in chat and ends up in logs. Mitigation: Add redaction, do not request prohibited data and restrict log access and retention.
- Failure: API outages cause silent failures and missed tickets. Mitigation: Implement retries, dead letter queues and alerting for failed workflow runs.
- Failure: Costs spike due to excessive AI calls. Mitigation: Use short prompts, cache known answers and route only relevant messages to the model.
How do you move from a simple bot to fully automated customer support?
Scaling is mostly about adding structure and operational discipline. A mature support bot usually includes:
- Multi channel coverage, web chat, WhatsApp, Slack or Teams, sometimes voice.
- Context retrieval, pull customer tier, open invoices, recent tickets and product plan before replying.
- Queue aware routing, route by intent, priority and skills, not just first available.
- Lifecycle automation, confirmations, follow ups, CSAT surveys and reopen logic.
- Analytics, containment, escalation reasons, sentiment trends and deflection opportunities.
Enterprise contact center stacks take this further with structured handoffs and transcript storage. For example Microsoft highlights routing with context variables, transcript retention and supervisor analytics for AI agents, which mirrors what we implement when we connect bots to CRMs and reporting pipelines: routing context. To see how this scales beyond support into broader operations, you can explore our overview of business process automation with n8n.
If you want help scoping your first workflow and mapping it to your CRM and support process, book a consultation with ThinkBot Agency here: book a consultation.
If you prefer to evaluate us through delivery history and client outcomes, you can also review our agency profile on Upwork.
FAQ
These are the most common questions we get when teams plan a chatbot that is connected to real operations, not just a chat interface.
What is the difference between a chatbot and an automated support workflow?
A chatbot is the conversation interface. An automated support workflow is the connected system behind it that creates tickets, updates CRM records, sends emails, routes to queues and logs actions with retries and monitoring.
How long does it take to build a production ready customer support bot?
A focused pilot for one workflow can be built in days, but production readiness usually takes several weeks. The extra time goes into integrations, data validation, escalation logic, logging, security and iterative testing with real conversations.
Can you integrate a chatbot with my CRM and email platform?
Yes. ThinkBot Agency regularly connects chat channels to CRMs and email platforms so leads and tickets are created or updated automatically, owners are assigned and follow ups are triggered without manual copy and paste.
Do I need n8n if I already have a chatbot platform?
Not always, but an orchestration layer like n8n becomes valuable when you need multi step routing, enrichment from multiple systems, reliable retries, audit logs and custom API connections that your chatbot platform cannot handle cleanly.
How do you prevent AI hallucinations in customer support?
We limit AI to tasks like intent detection and summarization, keep responses grounded in approved knowledge sources, add confidence thresholds and use safe fallbacks and human escalation for sensitive actions or low confidence cases.